Dns Server Configuration In Linux 6 Step By Step Pdf Converter
May 14, 2012 How to Configure Primary DNS Server in redhat 6 Step by Step Domain Name Server (DNS) Configuration and. AM Manage Linux Server DHCP,DNS,SMTP,Proxy. How to configure dns server in Linux step by step Guide, how to configure linux dns server step by step guide example and implementation.
Domain Name Service (DNS) is an internet service that maps IP addresses to fully qualified domain names (FQDN) and vice versa. BIND stands for Berkley Internet Naming Daemon. Gaeb Viewer Ohne Installation Of Laminate. BIND is the most common program used for maintaining a name server on Linux.
In this tutorial, we will explain how to install and configure a DNS server. If you are new to DNS, you should first understand the and how it works. Network Information In this tutorial, we are going to setup a local DNS server for the network shown in the below diagram. We’ll use “thegeekstuff.net” domain as an example for this DNS installation. “mail”, “web”, “ns” are the hosts that resides within this domain. It is possible to configure a single system to act as a caching name server, primary/master and secondary/slave.
We will configure this DNS as a Primay/Master as well as Caching DNS server. One reason I am looking into doing this is to get around the fact that Android devices do not support mDNS. On Windows and MAC, you can find devices with names like “mydevice.local” because they broadcast their names over mDNS. Unfortunately Android devices don’t support mDNS, but one way around it is to point such devices at a local DNS server that lists your devices.
Such a server should also act as an access point and/or bridge to the rest of the internet. Kind of annoying, really; I wouldn’t care if Android did not support mDNS since mDNS is actually a better solution to finding “named” devices on your local network. The article is as good as can be. Rockford Fosgate Fnx 2614 Manual Transmission. After all these years I wonder why this dns system must be so awkward. I have built some domains with dns and never liked that.
Instead of all those config and db files there could be just one csv file with columns like ‘mac’, ‘ip’, ‘name’, ‘role’, ‘comment’ Likewise the /etc/hostname file should contain a small csv table for all the NIC cards in the computer containing similar columns as above. It also needs columns for the IP-space connected to the cards. Many computers have different names and roles in different networks and it is awkward to build with the current system.
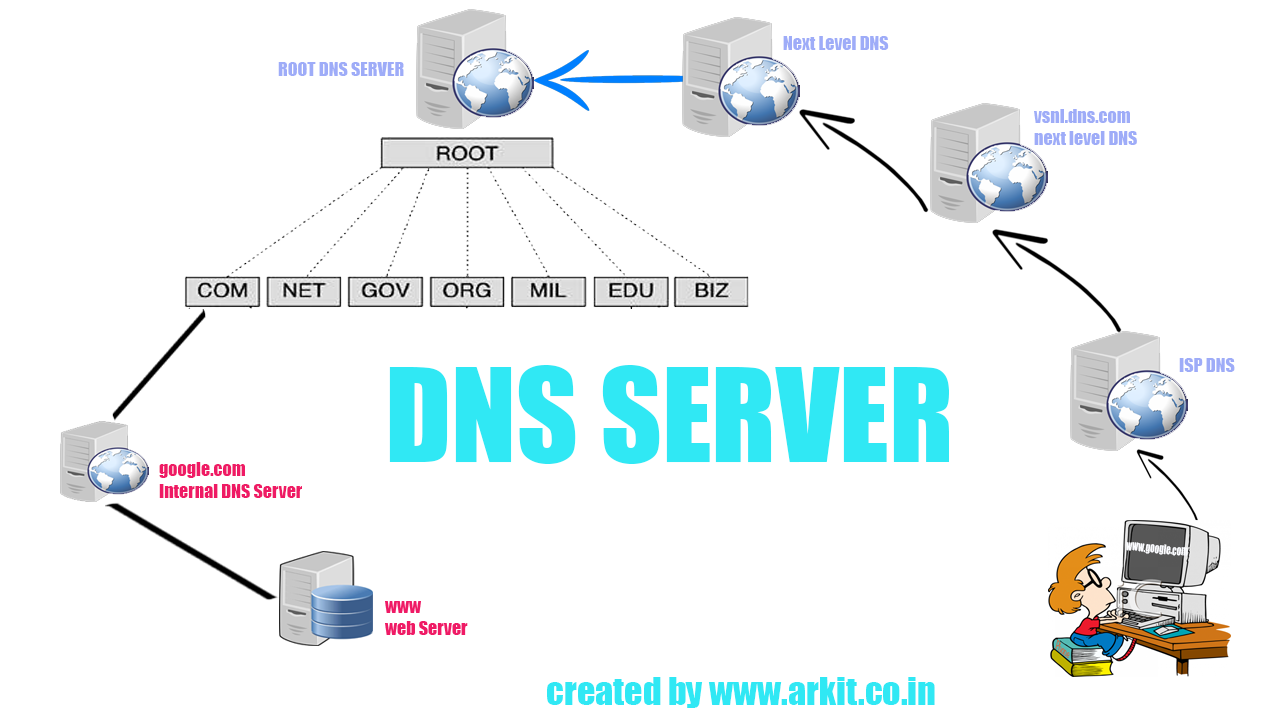
Domain Name Server (DNS) used for name resolving to any hosts. Master DNS servers ( Primary Server) are the original zone data handlers and Slave DNS server ( Secondary Server) are just a backup servers which is used to copy the same zone information’s from the master servers.
Master Server will resolve the names for every hosts which we defined in the zone database and use UDP protocol, because UDP protocols never use the acknowledgement process while tcp uses acknowledgement. DNS servers also use UDP protocols to resolve the query request at the earliest. Setup Master Slave DNS in RHEL/CentOS 6.5 How DNS Works? Understanding DNS might be little confusing for newbies. Here is a brief explanation on how the DNS work’s. Let’s say, if we need to access any website what we will do? Just type www.google.com in browser and hit enter.